The first projects on SARS-CoV-2 in lab-designed mini human organs gets underway
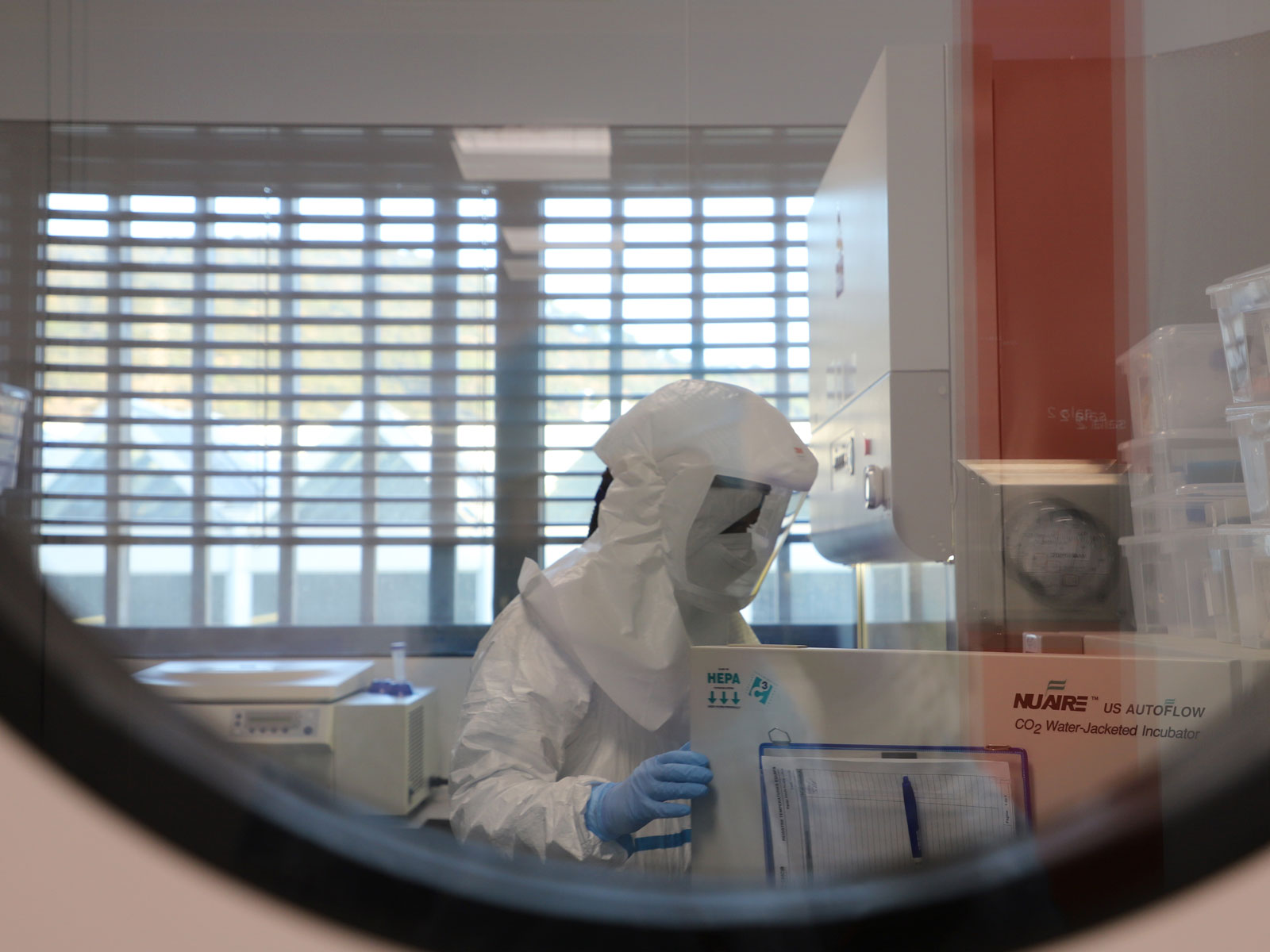
The Centre for Comparative Medicine and Bioimage of Catalonia (CMCiB), of the Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute (IGTP), will be the second centre in Catalonia to work on the SARS-CoV-2 virus obtained directly from patients. Until now most work has taken place with artificial viruses that can only infect once. Research staff of IrsiCaixa and the Institute of Evolutionary Biology (IBE) have started to work on the virus in the CMCiB to study the infection of organoids; mini organs designed in the laboratory to simulate human lungs and brains. Organoids are already being used in research and their use in studies into COVID-19 will provide better understanding of infection by SARS-CoV-2 and the capacity of different drugs to eliminate it from these tissues.